
Part 2: How to Setup Automated Batch Processing Pipeline for OpenAI API (GPT-4o-mini)

Introduction
Now a days utilising LLM’s for processing data on enterprise level has become a topic of dicussion . Lot of companies are heavliy investing in this segment of LLM finetuning , pre training , so that they are not left behind in the race .
But that being said LLM’s require a significant amount of investment , and even the cost for hosting an LLM or for inferencing is quite high due to the huge compute resource requirements of the LLM models .
In this blog we are going to explore , how we can process huge volume of data utilsing OpenAI API , we will be utilising supabase database to store the data . Supabase is a relational database .
If you are new to supabase , I will reccommend to get familiar with supabase , so that you can follow this tutorial with ease .
That being said , I am just using supabase here as an example , If you are experienced with utilising any kind of database may it be relational or non — relational databases , like AWS RDS (Relational Database service) , Dynamo DB (NoSql or Non-relational database) . You just have to implement the ingestion layer corresponding to your database .
I will be utilising python programming language and FastAPI framework , to build API’s , to ingest the data from the database , process the data to bring into the format required by OpenAI batch processing service .
I would also be utilising concepts such as triggers and database functions , and these would be written in PostgreSql , again if you are not familiar with it , no need to worry , I have added comments for each line which can be helpful to understand .
It would be useful if you can go through basics of SQL and get an understanding of SELECT , CREATE , FOR EACH , DELETE , etc .
You can go through resources like w3 schools or tutorials points or there are plenty of resources available on youtube as well .
Usecase : In this example, we will use gpt-4o-mini to extract movie categories from a description of the movie. We will also extract a 1-sentence summary from this description.
Now let’s see into how we can create the automated pipeline .
Step 1: Setup database functions and triggers using SQL editor provided by supabase
On the left side you will find an option to select SQL editor .
Once you are in the editor create a new snippet as you can in the above image .
Let’s first create the Batch processing function .
The purpose of this function would be to ingest the 1000(as supabase allows minimum 1000 rows in its fetch operation but it could be changed if you want it for enterprise you can check supabase documentation) rows of data , and pass this data to the API , an endpoint that we would create using FastApi .
Here is the PostgreSQL snippet
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION process_batch_data_v3()
RETURNS json AS $$
DECLARE
last_processed_id BIGINT;
current_batch_data json;
start_id BIGINT;
end_id BIGINT;
BEGIN
WITH batch_rows AS (
SELECT
imdb_id, -- row names
"Description",
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY imdb_id) as rn
FROM your_table_name
LIMIT 1000
)
SELECT
json_build_object(
'data', (SELECT array_to_json(array_agg(row_to_json(batch_rows)))) ,
'min_id', MIN(imdb_id),
'max_id', MAX(imdb_id)
)
INTO current_batch_data
FROM batch_rows;
PERFORM http_post(
'Our FastApi endpoint',
(current_batch_data)::text,
'application/json'
);
DELETE FROM your_table_name
WHERE id BETWEEN start_id AND end_id;
RETURN current_batch_data;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;Replace your_table_name with your actual table name that you have give for your table.
Just execute the above code and a data ingestion database function will be created for 1000 rows , which can be passed for batching using OpenAI API.
Once the rows are passed for batch processing those rows would also be deleted , for taking up next 1000 rows.(Another approach would be to add another column to add a check that batch processing for this row is completed.)
Now lets setup the database function for the trigger which would tell us when 1000 rows are available in our database .
Database function for Trigger
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION check_row_count()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
DECLARE
row_count integer;
BEGIN
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO row_count FROM your_table_name;
IF row_count = 1000 THEN
PERFORM process_batch_data_v3();
END IF;
RETURN NEW;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;Replace your_table_name with your actual table name .
Just execute the above code and your database function which would act as a trigger would be created .
Let’s setup the trigger for the above database function check_row_count().
CREATE TRIGGER check_row_count_trigger
AFTER INSERT ON imdb_dataset
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE FUNCTION check_row_count();Step 2: Let’s create the FastAPI endpoint which would pass the data received from the database functions .
You can run this endpoint locally or you can deploy this endpoint on hugging face spaces on docker and utilise it as a server .
I will give you the code for setting it up locally .
Lets first install all the libraries needed.
pip install supabase openai fastapi python-dotenv uvicorn
Here is the code below
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
import os
import json
import io
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from supabase import create_client, Client
from openai import Client as OpenAIClient
import logging
app = FastAPI()
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()
# Initialize OpenAI client
client = OpenAIClient(api_key=os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY'), organization=os.getenv('ORG_ID'))
# Initialize Supabase client
url: str = os.getenv('SUPABASE_URL')
key: str = os.getenv('SUPABASE_KEY')
supabase: Client = create_client(url, key)
@app.post("/test/v1")
async def testv1(request: Request):
system_prompt = '''
Your goal is to extract movie categories from movie descriptions, as well as a 1-sentence summary for these movies.
You will be provided with a movie description, and you will output a json object containing the following information:
{
categories: string[] // Array of categories based on the movie description,
summary: string // 1-sentence summary of the movie based on the movie description
}
Categories refer to the genre or type of the movie, like "action", "romance", "comedy", etc. Keep category names simple and use only lower case letters.
Movies can have several categories, but try to keep it under 3-4. Only mention the categories that are the most obvious based on the description.
'''
dataset = await request.json()
tasks = []
for ds in dataset.get('data', []):
imdb_id = ds.get('imdb_id')
description = ds.get('Description')
task = {
"custom_id": f"task-{imdb_id}",
"method": "POST",
"url": "/v1/chat/completions",
"body": {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"temperature": 0.1,
"response_format": {
"type": "json_object"
},
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": system_prompt
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": description
}
],
}
}
tasks.append(task)
# Write tasks to a JSON object
json_obj = io.BytesIO()
for obj in tasks:
json_obj.write((json.dumps(obj) + '\n').encode('utf-8'))
# Create a batch job
batch_file = client.files.create(
file=json_obj,
purpose="batch"
)
batch_job = client.batches.create(
input_file_id=batch_file.id,
endpoint="/v1/chat/completions",
completion_window="24h"
)
save_data = {
'batch_job_id': batch_job.id,
"batch_job_status": False
}
# Save batch job details to Supabase
response = supabase.table("batch_processing_details").insert(save_data).execute()
return {'data': 'Batch job is scheduled!'}
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)So above is the code utilising fastapi and openai batch processing .
I will explain what exactly the code does , so the below part of the code
dataset = await request.json() extracts the data from the sent from the database function.
tasks = []
for ds in dataset.get('data', []):
imdb_id = ds.get('imdb_id')
description = ds.get('Description')
task = {
"custom_id": f"task-{imdb_id}",
"method": "POST",
"url": "/v1/chat/completions",
"body": {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"temperature": 0.1,
"response_format": {
"type": "json_object"
},
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": system_prompt
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": description
}
],
}
}
tasks.append(task)This code goes through each row and constructs a openai request json which is a required format for openai.
# Write tasks to a JSON object
json_obj = io.BytesIO()
for obj in tasks:
json_obj.write((json.dumps(obj) + '\n').encode('utf-8'))Above code loads json required to pass for batch process in memory without requiring to save it locally or even on a cloud bucket . But this depends on the amount of data you would ingest and as long as you have enough memory on server as well .
# Create a batch job
batch_file = client.files.create(
file=json_obj,
purpose="batch"
)
batch_job = client.batches.create(
input_file_id=batch_file.id,
endpoint="/v1/chat/completions",
completion_window="24h"
)
save_data = {
'batch_job_id': batch_job.id,
"batch_job_status": False
}
# Save batch job details to Supabase
response = supabase.table("batch_processing_details").insert(save_data).execute()Above code is a standard code for creating a batch job where we pass the in-memory json object we have created , and then we create the batch by client.batches.create with , completion endpoint and completion_window parameters .
Now we extract the batch job id , and we will save this data onto a seperate table batch_processing_details , that you will have create along with columns batch_job_id , batch_job_status , id , created_at .
You can run the above code using below command
python your_file_name.pyyou will get the endpoint below one you run the command locally .

Now you have to pass the endpoint I have given below to your database function . Here is the endpoint .
http://0.0.0.0:8000/test/v1You have to pass the endpoint in this database function .
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION process_batch_data_v3()
RETURNS json AS $$
DECLARE
last_processed_id BIGINT;
current_batch_data json;
start_id BIGINT;
end_id BIGINT;
BEGIN
-- Get the batch data
WITH batch_rows AS (
SELECT
imdb_id,
"Description",
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY imdb_id) as rn
FROM imdb_dataset
LIMIT 1000
)
SELECT
json_build_object(
'data', (SELECT array_to_json(array_agg(row_to_json(batch_rows)))) ,
'min_id', MIN(imdb_id),
'max_id', MAX(imdb_id)
)
INTO current_batch_data
FROM batch_rows;
PERFORM http_post(
-- pass the endpoint here as given
'http://0.0.0.0:8000/test/v1',
(current_batch_data)::text,
'application/json'
);
DELETE FROM your_table
WHERE id BETWEEN start_id AND end_id;
-- Return the batch data
RETURN current_batch_data;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;Replace your_table_name with your actual table name .
Run this code again on the SQL editor tp update the function with desired endpoint .
Step 3: Setup the Supabase Database with IMDB data
Note: If you already have a different database filled with data, then you can just skip this step.
Let’s dowload the data and store it into supabase .
You can download your data here: Dataset
You may have to modify the dataset as it contains one empty column when you download it .
If you are new to supabase then you may have to create a new project and add a new table . You can just go through this 2 mins tutorial : tutorial
Above tutorial will show you to setup the project and create tables .
Now create a table with these columns imdb_id(as primary key) , created_at (Both these columns would be already present just rename id as imdb_id) , Title , Certificate , Duration , Genre , Rate(datatype float8) , Metascore(int8) , Description(text) , Cast(text) , Info(text) .
Now upload your csv data that you had downloaded .
Go to Insert>Import Data from CSV , as shown below.
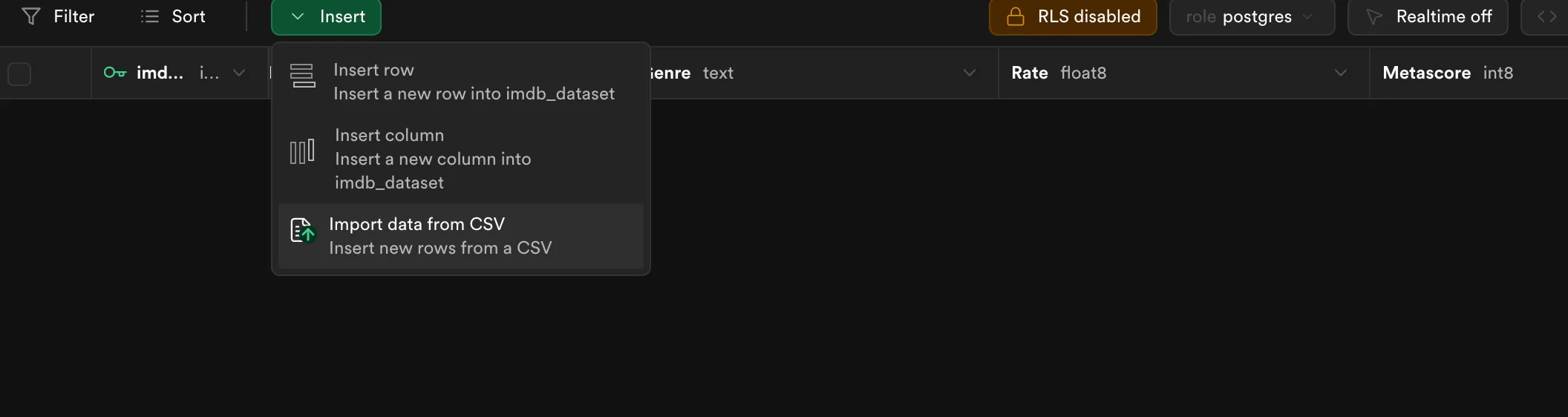
Now upload your data , by clicking on browse .
Once the whole 1000 rows are uploaded , the database function would be triggered and the 1000 rows data would be passed to the endpoint , and they would be sent for batch processing .
Conclusion
This completes the part 2 , In the part 3 , we will see in the next part how we would extract the completed output file and monitor if the batch process has been completed or not . We would use cron job to check if the batch process is completed or not and we would again setup a FastAPI endpoint that would be used to extract the completed batch job results and upsert our data into the database .
Connect with Hushh
Say something to reach out to us


Connect with hushh
Say something to reach out to us